This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Phylogeny
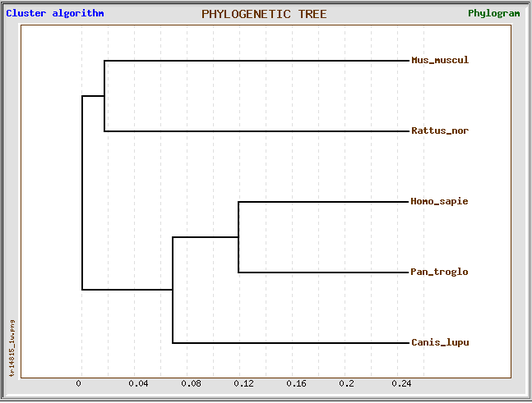
Phylogeny.fr phylogenetic tree
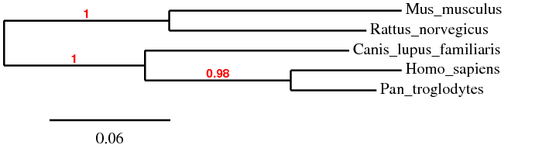
The figure below shows the phylogenetic tree that was obtained using the "One-click mode" on the program Phylogeny.fr. This particular mode allows the software to make decisions on your behalf based on the set of sequences submitted, optimizing the results for your data. The Homo sapiens HLA-DQA1 protein alignment was compared with the homologous proteins in Pan troglodytes, Canis lupus familiaris, Mus musculus, and Rattus norvegicus. This phylogenetic tree suggests that the human HLA-DQA1 protein is most related to the chimp HLA-DQA1 protein. The rat and mouse HLA-DQA1 proteins are the most distant from the human protein.
GeneBee phylogenetic tree using ClustalW alignment
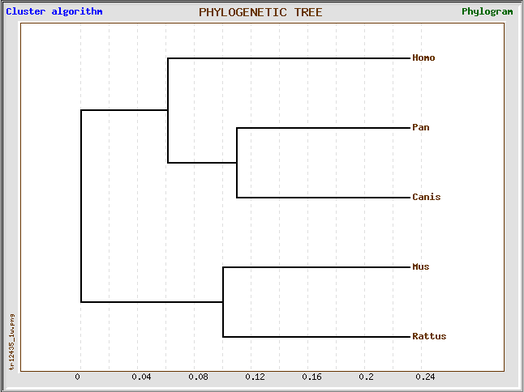
This GeneBee phylogenetic tree based on the ClustalW protein alignment produced similar results to the phylogeny.fr phylogenetic tree. The Human HLA-DQA1 protein was most closely related to the chimp and dog proteins. The mouse and rat HLA-DQA1 proteins were the most distant from the human HLA-DQA1 protein.
GeneBee phylogenetic tree using T-COFFEE alignment
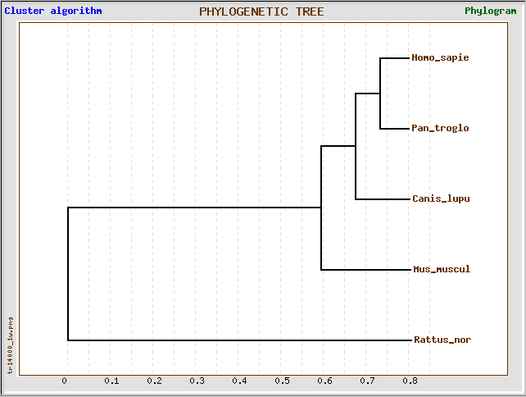
This GeneBee phylogenetic tree based on the T-COFFEE protein alignment, while slightly different, also produced similar results to the previous trees. The chimp and human HLA-DQA1 proteins were found to be the most closely related. The mouse and rat HLA-DQA1 proteins were the most distant from the human HLA-DQA1 protein.
GeneBee phylogenetic tree using MUSCLE alignment
This GeneBee phylogenetic tree based on the MUSCLE protein alignment also produced similar results to the above trees. The human HLA-DQA1 protein was most related to the chimp HLA-DQA1 and the mouse and rat HLA-DQA1 proteins were the most distant from the human HLA-DQA1 protein.
Analysis
Phylogeny.fr and GeneBee were used to create the various phylogenetic shown above. Both were reasonably easy to use, each using a slightly different input method. Phylogeny.fr allowed for the ease of submitting only the protein sequences for the homologous proteins as an input, as opposed to GeneBee, which requires the protein sequence alignments generated through other programs (ie. ClustalW, T-Coffee, or MUSCLE). Based on this input requirement, I would conclude that Phylogeny.fr is a much easier program to obtain a phylogenetic tree from.
Due to the fact that Phylogeny.fr uses the MUSCLE alignment program, I decided to compare the results obtained using this program and those obtained with GeneBee using the MUSCLE alignment. The data obtained from these programs produced trees with the same order of branches, differing slightly in the distances between the branch points. Since slightly different results were produced using the same alignment program, I do not think that the differences obtained are due to the data input, but rather the different methods used by Phylogeny.fr and GeneBee.
When using GeneBee, I submitted all of the protein sequence alignments that I obtained using the following programs: ClustalW, T-Coffee, and MUSCLE. While all differing slightly, the three alignments provided me with generally similar phylogenetic trees. ClustalW and MUSCLE had the most similar trees based on the order of the branches, giving only slight differences in the divergence of the Pan troglodytes. The T-Coffee alignment showed greater differences in the distances between branch points, as well as a difference in the divergence of the Mus musculus.
Due to the fact that Phylogeny.fr uses the MUSCLE alignment program, I decided to compare the results obtained using this program and those obtained with GeneBee using the MUSCLE alignment. The data obtained from these programs produced trees with the same order of branches, differing slightly in the distances between the branch points. Since slightly different results were produced using the same alignment program, I do not think that the differences obtained are due to the data input, but rather the different methods used by Phylogeny.fr and GeneBee.
When using GeneBee, I submitted all of the protein sequence alignments that I obtained using the following programs: ClustalW, T-Coffee, and MUSCLE. While all differing slightly, the three alignments provided me with generally similar phylogenetic trees. ClustalW and MUSCLE had the most similar trees based on the order of the branches, giving only slight differences in the divergence of the Pan troglodytes. The T-Coffee alignment showed greater differences in the distances between branch points, as well as a difference in the divergence of the Mus musculus.
References
- Phylogeny.fr: http://www.phylogeny.fr/
- GeneBee: http://www.genebee.msu.su/genebee.html